Bearing types and their applications in Wind
Malloy works closely with the largest bearing manufacturers in the world. These companies have been involved in the Wind industry for several years. The combination of their research and development and many years of experience in Wind has helped them develop solutions to the problems found in the industry.
Cylindrical roller bearings are a commonly used bearing type in Wind gearboxes. A cylindrical roller bearing has line contact providing more surface area to carry a given load which leads to much higher load ratings than a deep groove ball bearing.
Characteristics of various CRB types:
Separable vs. Non-Separable
In a separable bearing (N, NU, NF, NJ) the inner or outer ring can be removed from the bearing assembly. In an NU or NJ for example this allows the user to install the inner ring on the shaft and install the outer ring, roller set and cage assembly in the gearbox housing, and reassembly is as simple as sliding the shaft with inner ring back in the center of the roller/cage assembly. Separable bearings are found in most Wind gearboxes in High Speed Shaft and Intermediate Shaft positions.
Non-Separable bearings (NCF, NNCF) do not allow removal of the inner or outer ring. These bearings are common in Planet Carrier, Planets and Low Speed Shaft positions of a Wind gearbox.
Caged vs. Full Compliment
Caged (N, NU, NF, NJ) bearings have a cage separating the rollers. Caged cylindrical bearings are often found in Wind gearboxes on the High Speed Shaft and High Speed Intermediate Shaft because the roller separation provided by the cage prevents roller to roller smearing in these medium and high speed applications.
Full Compliment (NCF, NNCF) bearings do not have a cage separating the rollers. Full Compliment bearings are able to have extra rollers because of the space saved by not having a cage. More rollers of course leads to a higher load rating than a comparibly sized caged earing. These are often found in Wind gearboxes in the Planet Carrier and Low Speed Shaft positions. These positions travel at low enough speeds that roller to roller smearing is less of a concern and increased load capacity because of the extra rollers is beneficial.
Semi-Locating vs Non-Locating
Non-Locating bearings (N, NU) have a ring that can be removed from both sides of the assembly they will support no thrust loading. Non-Locating bearings are always paired with a locating bearing which will support axial loads and keep the shaft assembly in the correct position. These are commonly found in High Speed Shaft and Intermediate Shaft positions of a Wind gearbox. The most common example is 2 NU bearings on a shaft with a QJ bearing, where the QJ acts as the locating bearing. Another common configuration is 1 NU bearing on a shaft with a tapered set. Here the tapered set is acting as both a locating bearing and a radial bearing.
Semi-Locating bearings (NF, NJ, NCF, NNCF) have flanges on both sides of one ring, and only one side of the other ring. These bearings may be separable (NF, NJ), or non-separable (NCF, NNCF). These flanges are not intended to carry high thrust loads but can handle moderate thrust loads to ensure proper positioning of the shaft. These Semi-Locating bearings are always used together with another Semi-Locating bearing, back to back or face to face on opposite sides of a shaft. A common example in wind is NCF bearings on both sides of the planet carrier.
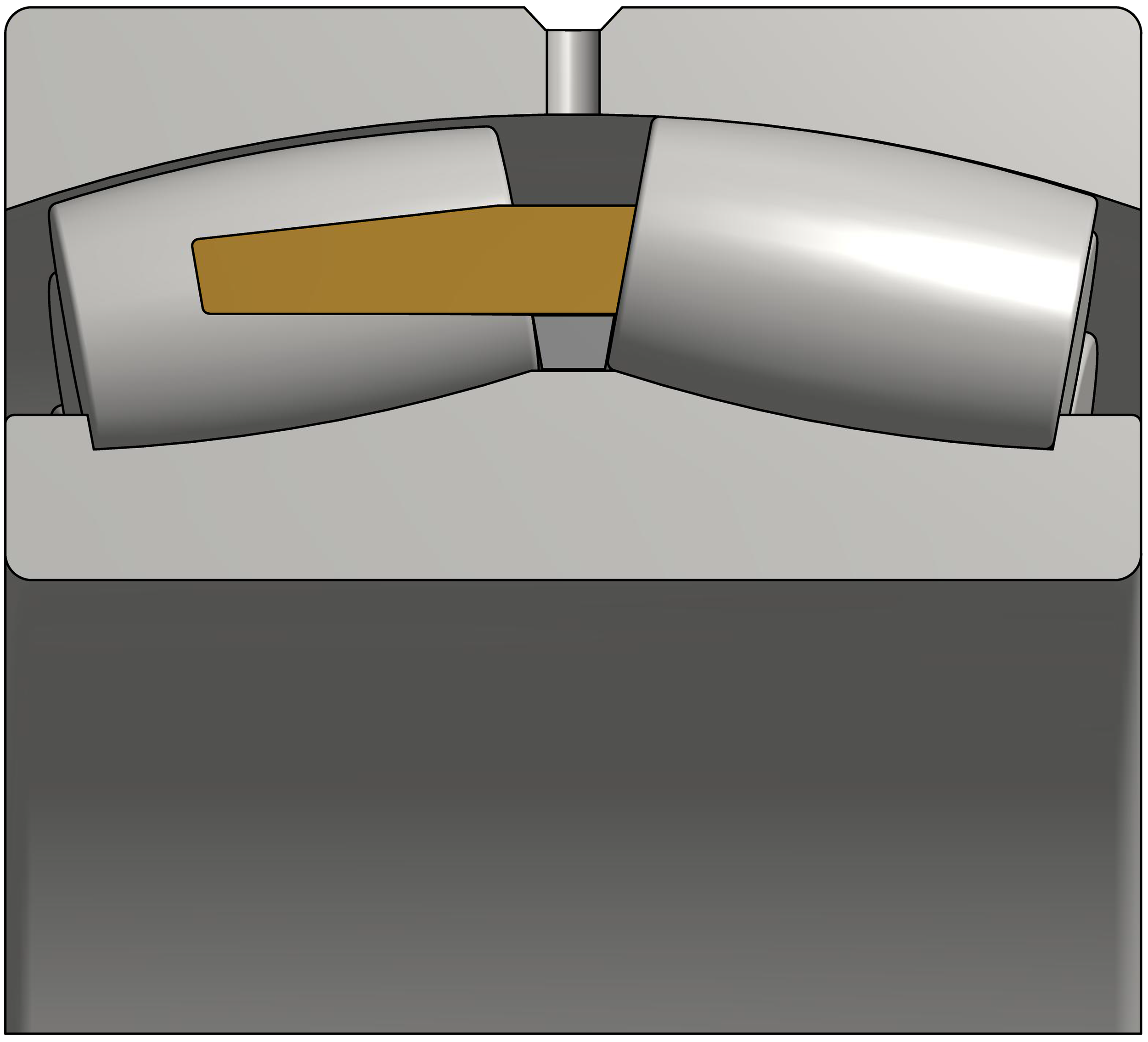
Spherical roller bearings have two rows of barrel shaped rollers. The outer race is formed as a sphere with the center on the central axis of a bearing, this makes an SRB self aligning. Spherical bearings are found in the main shaft position of most Wind tower applicatons.
Characteristics of Spherical Roller Bearings:
High Capacity
Double Row Self Aligning
Some thrust loading
Tapered roller bearings have tapered inner and outer races as well as tapered rollers. Tapered roller bearings are designed to handle combination axial and radial loads. Tapered bearings are always used in pairs facing opposite directions, sometimes one on each end of a shaft, or sometimes as a combined set in a face-to-face or back-to-back position. Single opposing Tapered bearings are used in some Wind gearboxes on the planet carrier. Tapered set bearings are used in several designs of Wind gearboxes as the locating and thrust bearing on High Speed Shaft, High Speed Intermediate Shaft and Low Speed Intermediate Shaft positions.
Characteristics of Tapered Roller Bearings:
High Capacity
Combined axial and radial loading
Adjustable preload or clearance
This type of bearing looks simlar to a traditional deep groove ball bearing. The difference is that it has a split inner ring and internal geometry changes to make this bearing capable of handling axial loads in both directions. These are used in many Wind gearbox designs as the locating and thrust bearing on a High Speed Shaft, or High Speed Intermediate Shaft.
Characteristics of 4 Point Angular Ball Bearings:
High Capacity
Thrust loading
Related content
-

Super Tough Bearings
From the steel alloy to the heat treatment, Super Tough bearings are upgraded for the most demanding applications.
-

Black Oxide Bearings
Black oxide coating and why it is used.
-

Through Hard vs Case Hard Bearings
Case hardened bearings have several benefits over the standard though hardened bearings. Read more about how and why here.
-

Blade Bearings
Solutions for failing blade bearings on all platforms.
-

NSK Bearings
Learn more about NSK Wind products here
-

IMO Slewing Bearings
IMO has produced over 90,000 slewing bearings for use in Pitch, Yaw and Single Main Bearing applications in Wind.
-

SKF Bearings
Learn more about SKF Wind products here