Bearing Clearance
By Cory Mittleider on 8/21/17
When identifying a bearing one of the important characteristics is clearance. This value is a measurement of how much space or “play” is present between the rollers and rings when not mounted. In radial bearings like Cylindrical Roller Bearings (CRB), Spherical Roller Bearings (SRB), Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBB), this is measured radially (Fig. 1).
Fig 1. Radial internal clearance of a CRB
In Tapered Roller Bearing assemblies where 2 are used together this is measured in the axial direction (Fig. 2).
Fig 2. Axial clearance in tapered roller bearing set
Radial bearing clearance and why you need it
The radial internal clearance measurements discussed are for unmounted bearings. When the bearing is installed in the application and run, the internal clearance is reduced and is known as operational clearance. Most bearing types run best with a small amount of operational clearance.
The shaft fit, housing fit and operating temperature will control how much clearance remains during operation. In most applications, the inner ring of the bearing is an interference fit on the shaft, and the outer ring is a slightly loose fit in the housing. When the bearing is installed the the clearance is reduced because of the interference fit on the shaft.
If a bearing with too small internal clearance is selected for the application, the bearing elements are preloaded (negative clearance) (Fig. 3) and this will cause excess heat, and lead to premature bearing failure.
Fig 3. Radial preload of cylindrical roller bearing
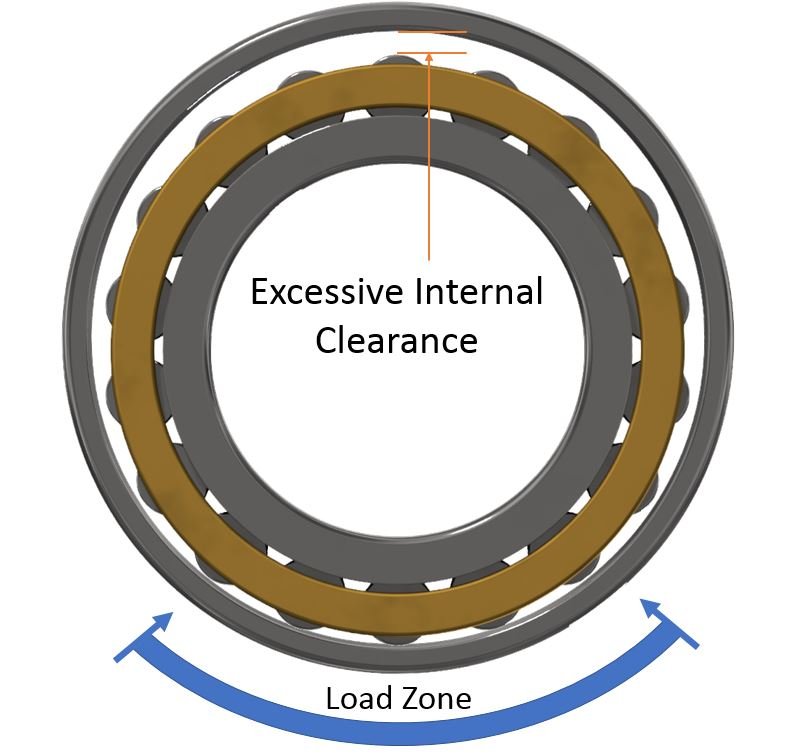
If a bearing with excessive clearance is selected, the operational clearance is too loose and can cause problems within the bearing. Since the load is carried by fewer rollers (Fig. 4) the effective load rating of the bearing is reduced. When the rollers are not in the load zone they are only guided by the cage. This allows them to skew slightly in the cage pocket or even roll at different speeds. When the rollers re-enter the load zone the radial load forces the rollers back to alignment and correct running speed, this can cause smearing damage.
Standards of measurement and nomenclature
Radial internal bearing clearance is measured in μm (micrometers), and is classified on a scale from small to large of C1, C2, CN, C3, C4, and C5.
The value of CN (C-Normal) a.k.a. C0 (C-Zero) is the default clearance, and thus is not indicated in the part number like every other clearance option will be. CN is appropriate for many every day applications with medium speed, medium load, and normal operating temperatures.
When large interference shaft fits are required, or the application runs at high speeds or in hot environment a larger clearance is needed like C3 or C4. C3 is a very common bearing clearance used in electric motors, generators and the high speed and intermediate positions of many gearboxes. C4 bearings are found in some Wind gearboxes on HSS positions with tight shaft and housing fits as well as some generators that notoriously run hot. C1 and C5 bearing clearances are not found in Wind applications.
Fig. 6 shows the clearance table for a Cylindrical Roller Bearing in the most common C2 - C4 ranges.
Fig. 6 Clearance table for cylindrical roller bearings
Special clearance nomenclature
When the running conditions can be controlled, or are very well known, the manufacturer may specify a special clearance. Depending on bearing manufacturer this may be called out in different ways. One way this may be indicated is as a Low/Medium/High suffix on the back of the standard nomenclature or example CNL, CNM, or CNH. In this nomenclature the full clearance range is broken up in to 4 quarters, and each of these ranges consists of 2 quarters. For example a common Planet Carrier bearing is an NCF 18/530 CNL. The full CN range of a cylindrical roller bearing with bore 530mm is 240-360μm (Fig. 6), so the CNL bearing has a clearance range of 240-300μm which is the lower 2 quarters of the full range (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7 Clearance ranges for NCF 18/530 by description
Other times the special bearing clearances are indicated in the full nomenclature of the part number. Another manufacturer of this bearing includes in their nomenclature “285”. This is the nominal (center) clearance, and they have a +/- window around this value. You will need to contact a trusted distributor like Malloy to determine the total range of possible clearances on this part number as it could be larger or narrower than the comparable NCF 18/530 CNL, but you can make an initial comparison based on this nominal value. (Fig. 8)
Fig. 8 Clearance range for NCF 18/530 by description compared to special nominal
There are some completely special part numbers that do not have any indication of clearance. Also one manufacturer uses C values higher than C5 which are not defined, and are just used to indicate a special clearance. In either case you’ll have to contact a bearing distributor like Malloy for more information.
Axial bearing clearance
In a tapered bearing set it is more feasible to measure axial clearance of the bearing during production and assembly than radial. This is done by fixing the bearing outer races in a housing, and clamping the inner races together, mounting a dial indicator to the housing, and moving the inner ring assembly up and down to measure total axial clearance.
There isn’t a table of predefined axial clearance value nomenclature like there is with radial internal clearance. This axial clearance is usually simply called out by the nominal value (e.g. 652 = 652μm).
Some tapered bearing sets include a spacer that has been inspected and machined to reach a specific axial clearance for a particular application. Other tapered bearing sets include a “green” spacer that is made to an approximate dimension but will need to be trimmed to fit during installation on the application. Either way axial clearance should always be checked during installation.
If you have any questions please give me a call at 605-357-1076
-Cory Mittleider